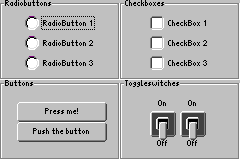
Der folgende Quelltext zeigt ein Beispielprogramm, dass alle drei Button-Typen verwendet, um eine ansonsten zweckfreie Benutzeroberfläche zu erstellen.
In Bild 1 ist ein Screenshot des WombatButtonExample-Programms dargestellt. Um das Beispielprogramm selbst auszuprobieren, öffnen Sie das Projekt WombatButtonExample, welches sich im Installationsverzeichnis der JControl/IDE unter "demos/cobra5329/WombatTutorial/WombatButtonExample" befindet (unter Windows: "C:\Programme\JControl\demos\cobra5329\WombatTutorial\WombatButtonExample).
| 1 | /** |
| 2 | * <p>This example demonstrates how to use buttons and similar components |
| 3 | * within the GUI framework JControl/Wombat.</p> |
| 4 | * |
| 5 | * <p>(C) DOMOLOGIC Home Automation GmbH 2007</p> |
| 6 | * |
| 7 | */ |
| 8 | import jcontrol.ui.wombat.Frame; |
| 9 | import jcontrol.ui.wombat.Container; |
| 10 | import jcontrol.ui.wombat.event.ActionListener; |
| 11 | import jcontrol.ui.wombat.Border; |
| 12 | import jcontrol.ui.wombat.RadioButton; |
| 13 | import jcontrol.ui.wombat.CheckBox; |
| 14 | import jcontrol.ui.wombat.Button; |
| 15 | import jcontrol.ui.wombat.ToggleSwitch; |
| 16 | import jcontrol.ui.wombat.event.ActionEvent; |
| 17 | |
| 18 | public class WombatButtonExample extends Frame implements ActionListener { |
| 19 | |
| 20 | |
| 21 | /** |
| 22 | * Constructor WombatButtonExample |
| 23 | */ |
| 24 | public WombatButtonExample() { |
| 25 | // create a container for the content of this frame |
| 26 | Container content = new Container(); |
| 27 | |
| 28 | // create borders and add them to the content |
| 29 | Border border1 = new Border("Radiobuttons", 40, 40, 120, 80, |
| 30 | Border.STYLE_ETCHED_BORDER); |
| 31 | content.add(border1); |
| 32 | Border border2 = new Border("Checkboxes", 160, 40, 120, 80, |
| 33 | Border.STYLE_ETCHED_BORDER); |
| 34 | content.add(border2); |
| 35 | Border border3 = new Border("Buttons", 40, 120, 120, 80, |
| 36 | Border.STYLE_ETCHED_BORDER); |
| 37 | content.add(border3); |
| 38 | Border border4 = new Border("Toggleswitches", 160, 120, 120, 80, |
| 39 | Border.STYLE_ETCHED_BORDER); |
| 40 | content.add(border4); |
| 41 | |
| 42 | /* create all components |
| 43 | add them to the content |
| 44 | and define an actionlistener for each component */ |
| 45 | |
| 46 | // Radiobuttons |
| 47 | RadioButton radioButton1 = new RadioButton("RadioButton 1", |
| 48 | 65, 56, 0, 0); |
| 49 | content.add(radioButton1); |
| 50 | radioButton1.setActionListener(this); |
| 51 | RadioButton radioButton2 = new RadioButton("RadioButton 2", |
| 52 | 65, 76, 0, 0); |
| 53 | content.add(radioButton2); |
| 54 | radioButton2.setActionListener(this); |
| 55 | RadioButton radioButton3 = new RadioButton("RadioButton 3", |
| 56 | 65, 96, 0, 0); |
| 57 | content.add(radioButton3); |
| 58 | radioButton3.setActionListener(this); |
| 59 | |
| 60 | // Checkboxes |
| 61 | CheckBox checkBox1 = new CheckBox("CheckBox 1", |
| 62 | 190, 56, 0, 0); |
| 63 | content.add(checkBox1); |
| 64 | checkBox1.setActionListener(this); |
| 65 | CheckBox checkBox2 = new CheckBox("CheckBox 2", |
| 66 | 190, 76, 0, 0); |
| 67 | content.add(checkBox2); |
| 68 | checkBox2.setActionListener(this); |
| 69 | CheckBox checkBox3 = new CheckBox("CheckBox 3", |
| 70 | 190, 96, 0, 0); |
| 71 | content.add(checkBox3); |
| 72 | checkBox3.setActionListener(this); |
| 73 | |
| 74 | // Buttons |
| 75 | Button button1 = new Button("Press me!", |
| 76 | 57, 142, 90, 20); |
| 77 | content.add(button1); |
| 78 | button1.setActionListener(this); |
| 79 | Button button2 = new Button("Push the button", |
| 80 | 57, 162, 90, 20); |
| 81 | content.add(button2); |
| 82 | button2.setActionListener(this); |
| 83 | |
| 84 | // Toggleswitches |
| 85 | ToggleSwitch toggleSwitch1 = new ToggleSwitch(190, 140); |
| 86 | toggleSwitch1.setText("On", "Off"); |
| 87 | content.add(toggleSwitch1); |
| 88 | toggleSwitch1.setActionListener(this); |
| 89 | ToggleSwitch toggleSwitch2 = new ToggleSwitch(220, 140); |
| 90 | toggleSwitch2.setText("On", "Off"); |
| 91 | content.add(toggleSwitch2); |
| 92 | toggleSwitch2.setActionListener(this); |
| 93 | /* */ |
| 94 | |
| 95 | // set the content to this frame |
| 96 | setContent(content); |
| 97 | // finally, make the frame visible |
| 98 | setVisible(true); |
| 99 | } |
| 100 | |
| 101 | /** |
| 102 | * This method is called every time any component declared above fires an |
| 103 | * action event. |
| 104 | * |
| 105 | * @param e the ActionEvent |
| 106 | */ |
| 107 | public void onActionEvent(ActionEvent e) { |
| 108 | // add some code if you want to |
| 109 | } |
| 110 | |
| 111 | |
| 112 | /** |
| 113 | * The main method. |
| 114 | * |
| 115 | * @param args |
| 116 | * The main arguments |
| 117 | */ |
| 118 | public static void main(String[] args) { |
| 119 | new WombatButtonExample(); |
| 120 | } |
| 121 | } |


 Buttons
Buttons